What is SCADA?
There exists a curious analogy between the enigma of SCADA and philosophy. There are many definitions of philosophy. The Aristotelian idea was that philosophy was all the existing knowledge. In the middle ages, theology was the first discipline to come apart from philosophy, acquiring its self identity. Then the arts, mathematics and geography followed. This has gone on until the present day, when a new concept of philosophy was developed: “philosophy is what remains after all the specialized branches come apart”. This is directly compared to SCADA: This generic term is used to describe systems with remote sensors, a communications channel and a system capable of storing said information e.g., a building’s alarm system is a SCADA, but for specific purposes. An alarm system has remote sensors for the intake of data. If an intruder tries to trespass a protected zone and the security system is activated, the alarm will go off ant the police will be notified. This action could be also performed manually by an operator. When the system reaches a certain level of specialization, it is identified by a name according to the functions to be performed. Other examples could be a smoke or fire or HVAC (Heating Ventilating Air Conditioning) detector system, i.e. SCADA is the generalization, what is left after the specialization and detachment of the particular systems.
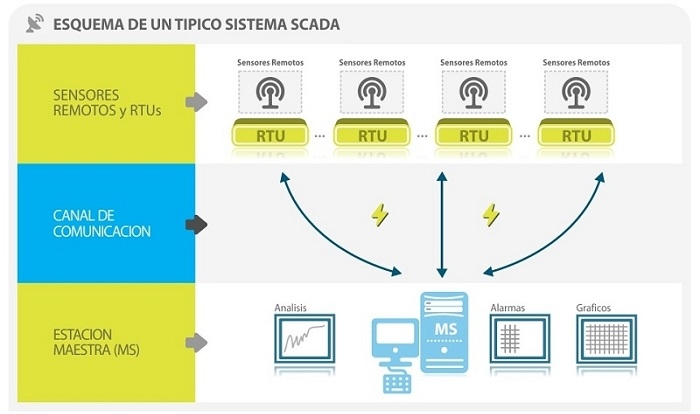
SCADA systems have been typically used by great organizations or industries in order to monitor very complex systems or processes. In the last years, the growing need and opportunity to monitor and control smaller systems providing the same product benefits but at a lower cost has emerged.
SCADA solutions have been typically reserved for big organizations, due to the high costs of personalization for each case in particular, including the sensors, the communication channels and the specific implementations. In the last years, and with the evolution of a great variety of new technologies, there is a new and growing need of this type of solutions for all kind of businesses. This situation makes this type of solutions accessible to a great number of users who have never before been able to face them as desired.
[Back to Top]



